梗概
- 工厂对象负责在不同的输入下返回不同的实例对象
- 假设我们有A,B,C三个类,我们需要根据不同的情况条件创建这三个类中的其中一个实例
- 这时,就有一段返回实例的判断逻辑,我们把这段逻辑封装在一个类中,这个类就叫工厂类
- 工厂方法是一个类对外的唯一入口
- child::工厂类的继承
详解
Java实现
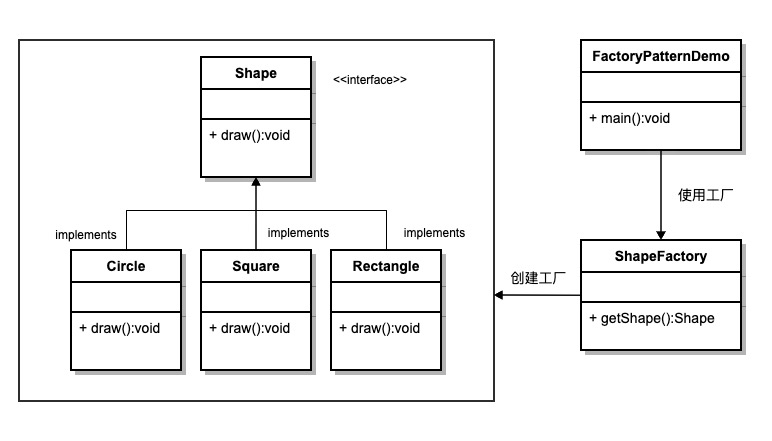
public interface Shape {
void draw();
}
public class Rectangle implements Shape {
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("Inside Rectangle::draw() method.");
}
}
public class Square implements Shape {
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("Inside Square::draw() method.");
}
}
public class Circle implements Shape {
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("Inside Circle::draw() method.");
}
}
public class ShapeFactory {
//使用 getShape 方法获取形状类型的对象
public Shape getShape(String shapeType){
if(shapeType == null){
return null;
}
if(shapeType.equalsIgnoreCase("CIRCLE")){
return new Circle();
} else if(shapeType.equalsIgnoreCase("RECTANGLE")){
return new Rectangle();
} else if(shapeType.equalsIgnoreCase("SQUARE")){
return new Square();
}
return null;
}
}
public class FactoryPatternDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ShapeFactory shapeFactory = new ShapeFactory();
//获取 Circle 的对象,并调用它的 draw 方法
Shape shape1 = shapeFactory.getShape("CIRCLE");
//调用 Circle 的 draw 方法
shape1.draw();
//获取 Rectangle 的对象,并调用它的 draw 方法
Shape shape2 = shapeFactory.getShape("RECTANGLE");
//调用 Rectangle 的 draw 方法
shape2.draw();
//获取 Square 的对象,并调用它的 draw 方法
Shape shape3 = shapeFactory.getShape("SQUARE");
//调用 Square 的 draw 方法
shape3.draw();
}
}输出
Inside Circle::draw() method.
Inside Rectangle::draw() method.
Inside Square::draw() method.